1. Signal lines and power lines must be separated to minimize interference from the inverter and other devices. When using analog signals to control an inverter remotely, it is essential to isolate the signal line from the inverter’s main circuit and control loop. These lines should maintain a distance of at least 30 cm, even within the control cabinet. The length between the signal line and the inverter should not exceed 50 meters.
2. To further reduce interference, signal and power lines should be placed in separate metal conduits or sleeves. In systems where two Fuji inverters are located 30m and 20m away from the control cabinet respectively, the signal cables connecting the PLC and inverter may not be in metal pipes, making them prone to interference. Additionally, since the inverters lack built-in reactors, their input and output stages can generate strong electromagnetic interference. Therefore, it's crucial to route the signal lines through metal tubes or hoses all the way to the inverter control terminals, ensuring complete separation from the power lines.
3. For analog control signals, it's recommended to use double-shielded twisted-pair cables with a wire size ranging from 0.5 to 2 mm². When stripping the cable, keep the exposed length as short as possible—about 5–7 mm. After stripping, wrap the shield with insulating tape to prevent contact with other equipment, which could introduce unwanted noise into the system.
4. To improve wiring simplicity and reliability, crimp terminals are strongly recommended for signal lines. A typical crimp terminal setup is shown below:
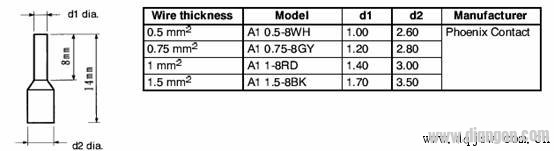
5. If crimp terminals are unavailable, ensure proper wiring techniques are followed. Refer to the wiring diagram below for guidance:
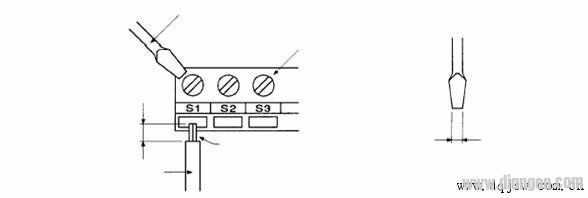
7. The inverter’s grounding should be separate from the PLC control circuit. If this isn’t possible, floating the control circuit ground can help reduce interference. However, the inverter must still be properly grounded. It’s also recommended to float both ends of the shielded analog signal cable. Since the PLC and inverter often share a common ground, it’s advisable to ground the PLC separately or connect it through insulation when feasible.
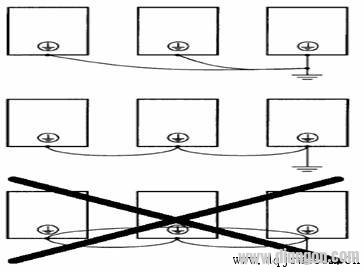
8. Inverter Grounding: For 400V-class inverters, C-type grounding is required (ground resistance ≤ 10Ω). Avoid sharing the grounding wire with welding machines or other high-power equipment. The grounding wire must meet the electrical standards, such as 22 mm² for a 35kW inverter and 50 mm² for an 87kW inverter. Keep the ground wire as short as possible to avoid unstable potential at the grounding point due to leakage current. When multiple inverters are used, do not form a loop in the grounding wire. See the diagram below:
9. When the distance between the inverter and motor is long, the harmonic leakage current from the cable can cause interference. To mitigate this, adjust the inverter’s carrier frequency based on the distance: - Up to 50m: 15kHz or lower - Up to 100m: 10kHz or lower - Over 100m: 5kHz or lower
CPVC Sheet Conical Twin Screw Extrusion Line
High Capacity Cpvc Sheet Conical Twin Screw Extrusion Line,Precision Cpvc Sheet Conical Twin Screw Extrusion Line,Affordable Cpvc Sheet Conical Twin Screw Extrusion Line,Customizable Cpvc Sheet Conical Twin Screw Extrusion Line
Zhejiang IET Intelligent Equipment Manufacturing Co.,Ltd , https://www.ietmachinery.com