The second phase of the 5G technology R&D tests has officially concluded successfully. But what exactly took place during the testing, and what were the key results? Let's dive in and explore.
At the "Second 5G Innovation and Development Summit Forum" held recently, Wei Kejun, Deputy Head of the Wireless Technology Working Group of the IMT-2020 (5G) Promotion Group, provided detailed insights into the frequency bands used for the 5G phase II test, the test systems involved, and the equipment manufacturers participating. He also shared the outcomes of the major scenarios tested in this phase.

Reporters interviewed industry players to gain a deeper understanding of the current status of the 5G phase II test across several major scenarios. These scenarios closely reflect real-world applications of 5G technology.
As we know, China launched the second phase of its 5G testing at the end of last year. This phase moved beyond single-point technical trials and focused on testing typical 5G scenarios. The goal was to achieve continuous wide coverage, high capacity in hotspots, low latency, high reliability, and support for massive machine-type communications (mMTC).
This phase involved not only traditional equipment vendors but also chip and instrument manufacturers, reflecting a broader industrial chain collaboration. The scenario-based testing is crucial for the commercial deployment of 5G, as it ensures that the technology meets real-world demands.
Notably, the IMT-2020 group applied for the 3.4GHz–3.6GHz low-frequency band last year. This year, with approval from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, three additional frequency bands—4.8–5.0GHz, 24.75–37.5GHz, and 37–42.5GHz—were added to the 5G R&D test.
The 5G R&D test system includes 12 specifications covering wireless and network testing, with 215 related test cases. It covers both high- and low-frequency mixed scenarios and includes core network requirements and test methods.
Several vendors participated in the testing. Huawei tested all scenarios, while ZTE completed all except the core network test. Ericsson and Datang each completed five tests, and Nokia Bell conducted tests on continuous coverage, low latency, and high reliability.
Chip and instrument manufacturers also engaged in docking tests. Keysight collaborated with five system manufacturers, including Huawei, Ericsson, ZTE, Datang, and Shanghai Nokia Bell. Rohde & Schwarz worked with Huawei, Ericsson, and ZTE, while Datang Lianyi partnered with Huawei and Datang. Intel, Ericsson, and Nokia Bell also conducted docking tests.
In the 5G core network test, Huawei completed all items, while Datang completed most. Ericsson, ZTE, and Shanghai Nokia Bell followed their planned testing schedules.
Overall, companies used open-source platforms like OpenStack to implement 5G core network functions, verifying key technologies such as service architecture, network slicing, and edge computing.
**Scene 1: Continuous Wide Coverage**
This scenario focuses on ensuring seamless high-speed connectivity for users, especially in challenging environments. The test results showed a single-user peak rate over 1.6 Gbps and a cell peak rate exceeding 10 Gbps, meeting ITU standards.
**Scene 2: Low Latency and High Reliability**
Designed for vertical industries like autonomous driving and industrial automation, the test achieved sub-1ms latency and near 100% reliability, meeting ITU requirements.
**Scene 3: Hotspot High Capacity (Low and High Frequency)**
This scenario targets dense areas requiring high data rates and traffic density. Results exceeded ITU benchmarks, with peak rates reaching up to 62.25 Gbps.
**Scene 4: Low Power and Large Connections**
Focused on IoT applications, this scenario verified the ability to support over 1 million connections per square kilometer, with ultra-low power consumption.
**Scene 5: High and Low Frequency Mixed Scene**
Testing hybrid scenarios revealed challenges with low-frequency uplink coverage, which need further optimization.
**Scene 6: Other Hybrid Scenarios**
The test verified an autonomous air interface architecture, supporting eMBB, uRLLC, and mMTC with flexible bandwidth allocation.
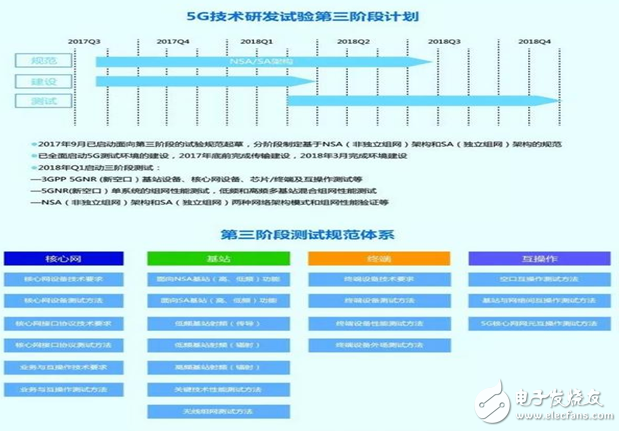
Looking ahead, the third phase of the 5G R&D test will begin in late 2017 and early 2018, focusing on commercial hardware and networking performance. This phase aims to align with global 5G standards and prepare for full-scale deployment.
Comcn Electronics Limited , https://www.comencnspeaker.com