[PConline News] Western Digital has solidified its position as the world's third-largest NAND flash memory supplier after acquiring a significant portion of SanDisk. However, the company hasn't abandoned its traditional HDD business, which has long been a major revenue driver. In fact, Western Digital continues to push the boundaries of hard disk technology. Today’s HDDs already exceed 10TB, 12TB, and even 14TB in capacity, and in the next two years, 16TB and 18TB drives are expected to hit the market. Despite facing technical challenges, Western Digital has announced a breakthrough: it will use MAMR (Microwave-Assisted Magnetic Recording) technology to boost storage density to 4 Tb per square inch—four times the current level. This could lead to 40TB HDDs by 2025.

Currently, most HDDs use PMR (Perpendicular Magnetic Recording), which has reached a density of 1 Tb per square inch. Improvements have been slow, and recent upgrades have relied on SMR (Shingled Magnetic Recording), pushing capacities up to 12TB and 14TB. Previously, 16TB and beyond were expected to rely on HAMR (Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording), which uses laser heating to write data. However, HAMR has faced delays due to high costs and complexity, including the need for specialized materials like iron and platinum, and the integration of lasers into the drive itself. The process requires temperatures of up to 400–700°C, which poses reliability and manufacturing challenges.
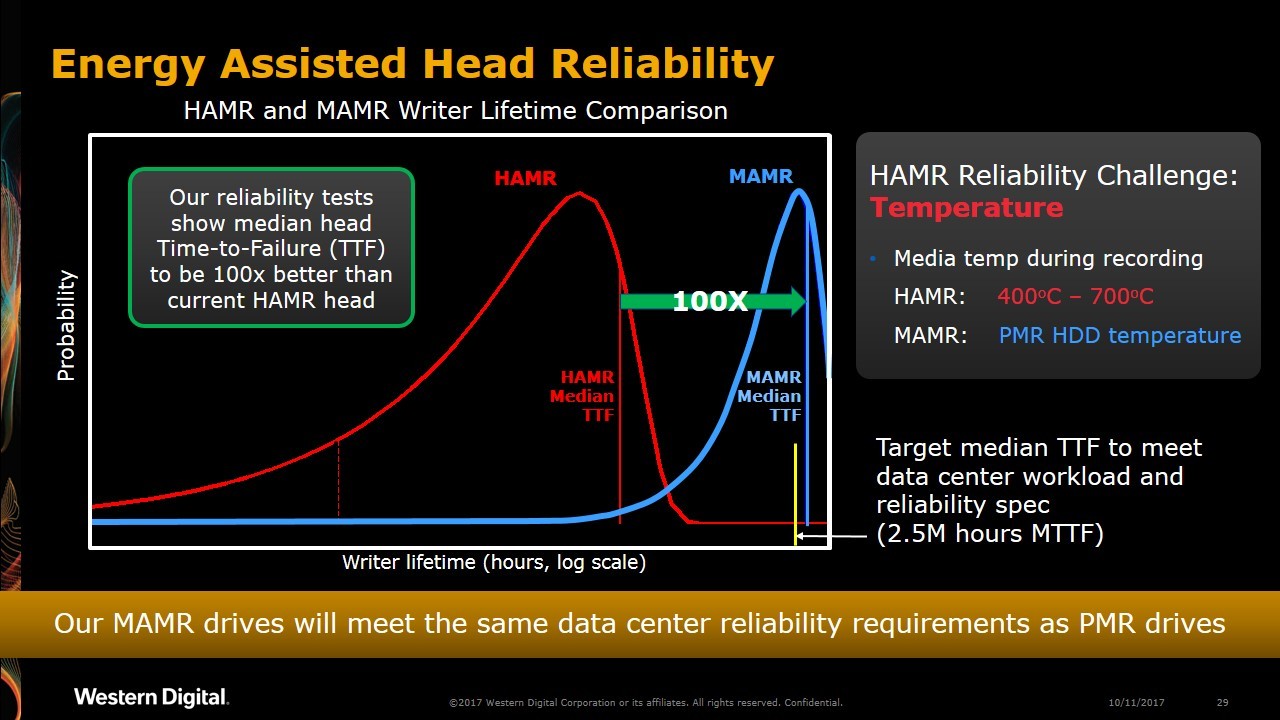
Although HAMR can increase storage density to around 5 Tb per square inch, it comes with significant drawbacks. It requires changes in media, heads, and manufacturing processes, making it expensive and less reliable. To address these issues, Western Digital has turned to MAMR, a more mature and cost-effective alternative. MAMR is also an energy-assisted magnetic recording technology, but instead of using lasers, it employs microwave components. This approach offers better reliability and lower costs compared to HAMR.
The MAMR technology was developed by Jimmy Zhu, a vice president at Western Digital and a researcher from Carnegie Mellon University. His work has led to the creation of a spin-torque oscillator (STO), which generates a microwave magnetic field to assist in writing data onto the disk. This method avoids the need for high-temperature heating, making it more efficient and stable.
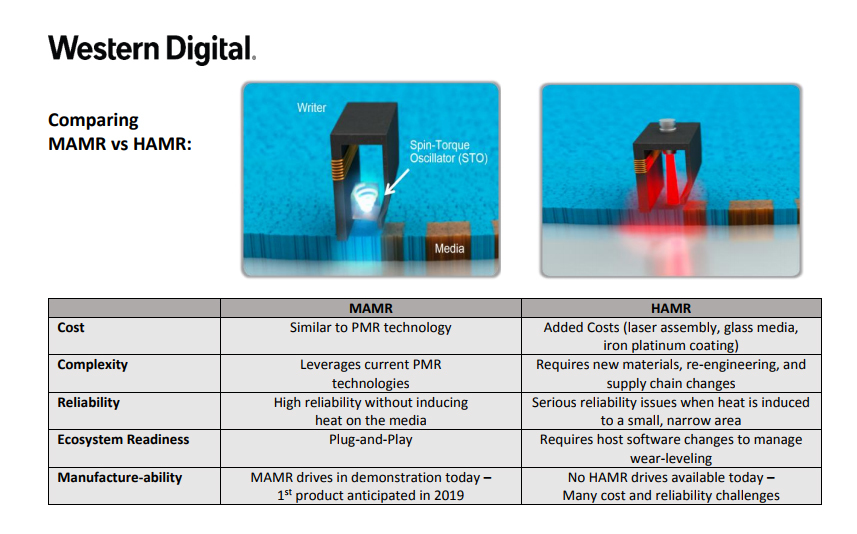
By replacing lasers with microwave components, MAMR simplifies the design and reduces costs. According to Western Digital, MAMR is nearly as cost-effective as traditional PMR technology, while offering 100 times the reliability of HAMR drives. For consumers, this means that the next generation of HDDs will be more affordable, durable, and capable of holding significantly more data. With MAMR, Western Digital aims to push HDD storage density to 4 Tb per square inch, potentially enabling 40TB drives by 2025.
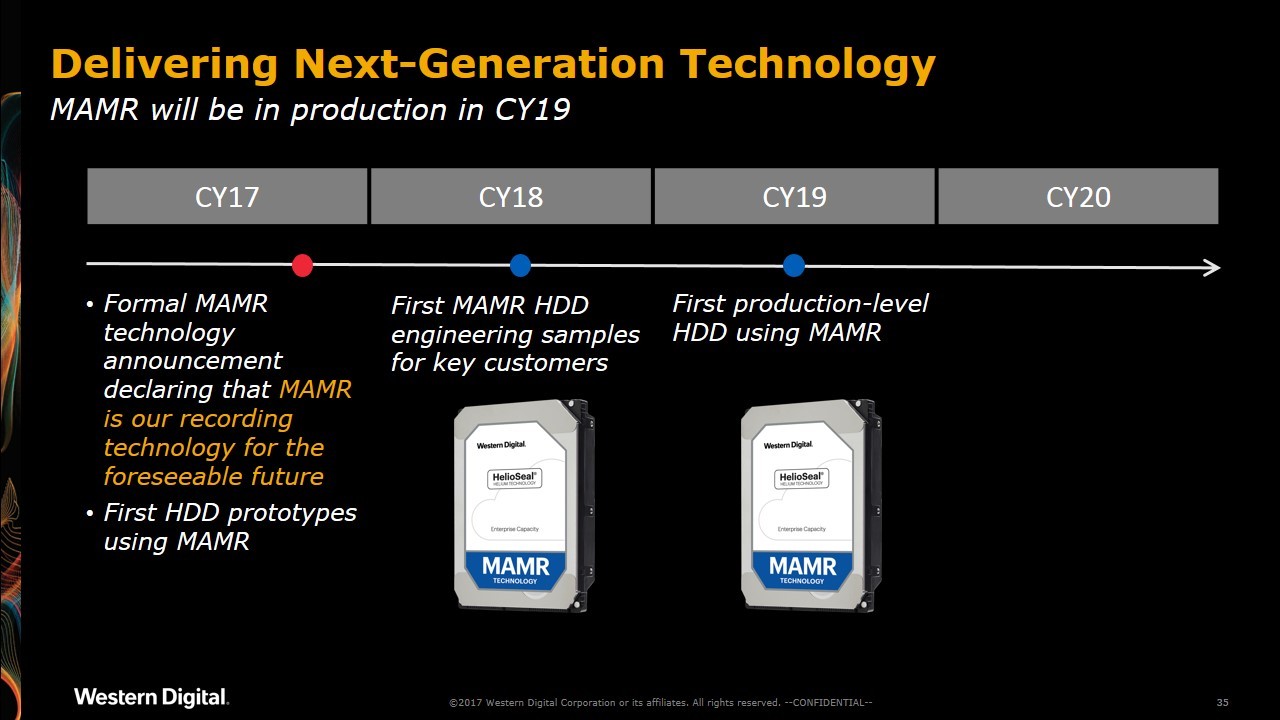
Western Digital began testing MAMR HDD prototypes in 2017, provided early samples to select customers in 2018, and officially launched the technology in 2019. This development marks a major milestone in the evolution of hard disk technology, ensuring that HDDs remain relevant in the era of SSDs and cloud storage.
Fiber Optical Patch Panel,Fiber Optic Patch Panel,Fiber Optic Patch Panel Accessories,Fiber Optic Patch Cord Adapter
Huizhou Fibercan Industrial Co.Ltd , https://www.fibercan-network.com