This article will explore the detailed process of how Layer 2 switches handle data forwarding within VLANs. By combining visual diagrams with textual explanations, we'll gain a clear understanding of how frames are structured and processed according to the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
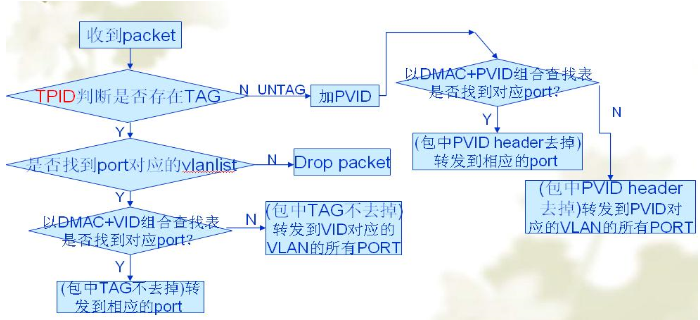
The image above illustrates the specific forwarding mechanism of a Layer 2 switch. Below is a more in-depth explanation of the steps involved.
First, let's take a closer look at what TPID stands for.
In the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN protocol, frames are structured as shown in the following diagram:
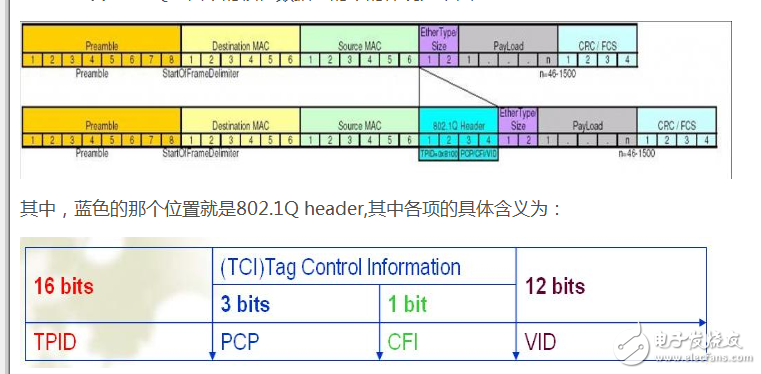
**Tag Protocol Identifier (TPID):** This is a 16-bit field that has a fixed value of 0x8100. It is used to identify frames that have been tagged with VLAN information. Similar to the Ethernet type field in untagged frames, it helps distinguish between tagged and untagged frames. If this value is 0x8100, the frame is recognized as a VLAN-tagged frame.
**Priority Code Point (PCP):** A 3-bit field used to indicate the priority level of the frame, ranging from 0 (lowest) to 7 (highest). This is part of the IEEE 802.1p standard for quality of service (QoS).
**Canonical Format Indicator (CFI):** A single bit field. When set to 1, it indicates that the MAC address is in a non-standard format, typically used when bridging between Ethernet and Token Ring networks. In most modern Ethernet switches, CFI is set to 0 by default.
**VLAN Identifier (VID):** A 12-bit field that identifies which VLAN the frame belongs to. The value 0x000 is reserved and indicates that the frame is not part of any VLAN. Values from 0x001 to 0xFFF are used to identify up to 4094 different VLANs.
Next, let's examine how the switch table works in a VLAN-enabled environment:
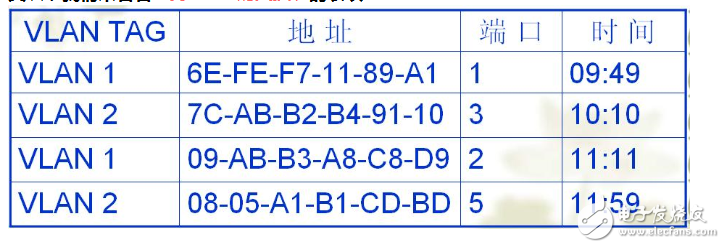
When a VLAN-enabled switch processes a frame, it uses the destination MAC address combined with the VLAN ID as the key to look up the appropriate port for forwarding. Like a regular switch, this table can be dynamically learned based on traffic patterns.
Finally, here are some additional terms you should be familiar with:
**PVID (Port VLAN ID):** When a port receives an untagged frame, it doesn’t know which VLAN to assign it to. The PVID defines the default VLAN for that port. Think of it as the default VLAN assigned to the port when no tag is present.
**TAGGED:** If a port is configured to send tagged frames, then all outgoing traffic from that port will include a VLAN tag. This is typical for trunk ports that connect to other switches or routers.
**UNTAGGED:** If a port is configured as untagged, the frames sent from that port will not have a VLAN tag. However, before sending, the switch adds the PVID to the frame so that it can be properly forwarded through the network.
By understanding these concepts, you’ll gain a deeper insight into how Layer 2 switches manage and forward traffic within VLAN environments.
Battery connector,battery holder,battery holder spring,power connector,connector
Dongguan Yiyou Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.dsubminiature.com