This article will explore the process of how Layer 2 switches handle data forwarding within VLANs. Through a combination of diagrams and explanations, we'll gain a clearer understanding of how frames are structured according to the 802.1Q VLAN protocol.
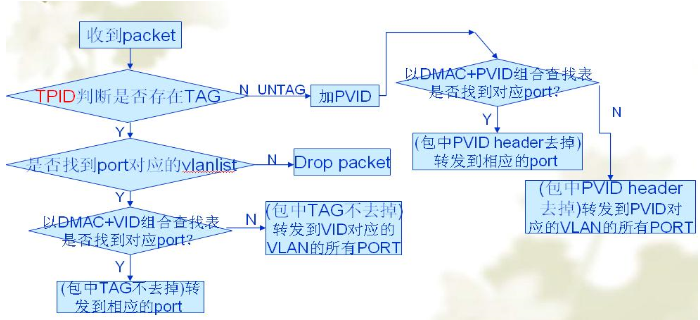
The image above illustrates the detailed forwarding mechanism of a Layer 2 switch. Let's go through each part of the diagram step by step.
First, let's take a closer look at what TPID stands for. In the context of the 802.1Q VLAN protocol, the frame is structured as shown in the following diagram:
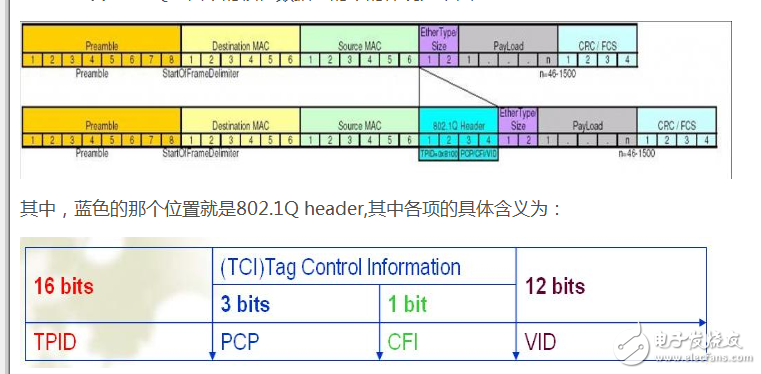
**Tag Protocol Identifier (TPID):** This is a 16-bit field that has a fixed value of 0x8100. It identifies an Ethernet frame as being tagged with VLAN information. This field serves a similar role to the Ethernet type or length field in untagged frames, helping to distinguish between standard and VLAN-tagged frames.
**Priority Code Point (PCP):** A 3-bit field used to indicate the priority level of the traffic, ranging from 0 (lowest) to 7 (highest). This helps in prioritizing different types of data streams.
**Canonical Format Indicator (CFI):** A single bit that indicates whether the MAC address in the frame is in a standard format (0) or a non-standard one (1). In most Ethernet environments, this is set to 0 by default.
**VLAN Identifier (VID):** A 12-bit field that specifies which VLAN the frame belongs to. The value 0 is reserved and typically represents a frame without VLAN tagging. Values from 1 to 4094 can be used to identify up to 4094 unique VLANs.
Next, let’s examine how the switch table works in a VLAN-enabled environment:
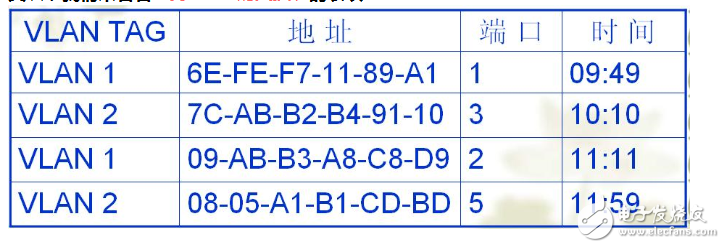
In a VLAN-aware switch, the lookup key for the switch table is usually the destination MAC address combined with the VLAN ID. This allows the switch to determine the correct port to forward the frame to. Like a regular switch, this table can also be learned dynamically based on incoming traffic.
Finally, here are some additional terms you should understand:
**PVID (Port VLAN ID):** When a frame arrives at a port without a VLAN tag, the PVID defines which VLAN the frame should belong to. Essentially, it acts as the default VLAN for that port.
**TAGGED:** If a port is configured to handle tagged frames, any outgoing frame from that port will include a VLAN tag. This ensures that the receiving device knows which VLAN the frame belongs to.
**UNTAGGED:** If a port is set to untagged mode, the outgoing frame will not have a VLAN tag. However, before sending, the switch will add the PVID to the frame so that it can be properly processed by other VLAN-aware devices.
Understanding these concepts is essential for managing and troubleshooting networks that use VLANs effectively.
D-subminiature Connector,D-Sub Connector,Power D-Sub,D-Sub Power Connector,High Power D-Sub Connector,db9,db15,db25,ip67 D-Sub,waterproof D-Sub connector,D-Sub connector female,D-Sub male connector
Dongguan Yiyou Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.dsubminiature.com