The advantages of wireless charging for portable devices go far beyond the shackles of cables. As early as 2013, smart phone manufacturers began to integrate wireless charging in their smartphones. In the future, the wireless charging function of mobile devices is expected to be as popular as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
In June 2015, the Alliance for Wireless Power (A4WP) and the Power Matters Alliance (PMA) merged to form the AirFuel Alliance. This merger has accelerated the vision of future consumers, where devices will be interoperable and convenient.
Near field inductive charging
Nikola Tesla first demonstrated near-field or magnetic resonance charging in the 1880s, transmitting energy through an oscillating magnetic field (Fig. 1).
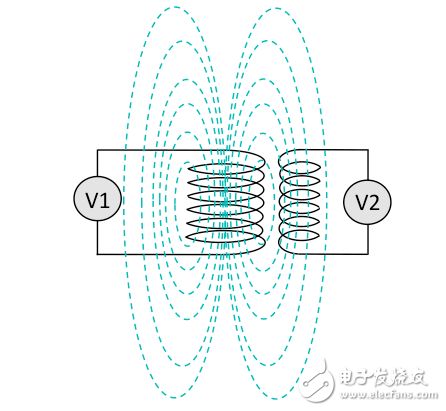
Figure 1 shows the magnetic resonance diagram
The current and voltage delivered from the transmitter to the receiver must be alternating current. A charging pad that acts as a transmitter draws power from a wall outlet, steps down the AC grid voltage and converts it to DC, providing bias to the transmitter's driver and controller circuitry. The driver and controller generate a switching signal and can adjust the switching frequency to convert the direct current into alternating current and input it to the primary side coil.
On the receiver side, the AC power is rectified and adjusted by synchronous switching to charge the battery. The frequency in the coil changes depending on the amount of power required by the receiver. The communication signal is superimposed on the power signal, so both know that the device has been placed on the charging pad. Inductive charging is more efficient, but it is very sensitive to whether the coil is aligned. The coupling coil needs to be adjusted to slightly deviate from the resonant frequency to optimize power transfer (Figure 2).
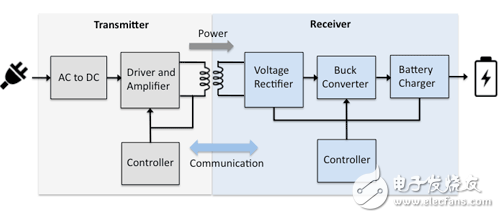
Figure 2 Near-field inductive charging system
The Qi developed by the Wireless Power ConsorTIum (WPC) is one of the mainstream near-field wireless charging standards, and the community includes more than 200 companies. AirFuel proximity magnetic induction (InducTIve) is another standard. Powermat is a good example of bridging technology that provides a universal ring that can be used with a charging pad to charge a portable device.
Near field resonance charging
Resonance charging is another form of near-field charging that works the same as an electromagnetic field, but requires a front end of the resonator (Figure 3). The standard is dominated by AirFuel Resonant, allowing for a shorter distance between the transmitter and receiver. A single 6.78MHz transmitter can support multiple receivers without physical alignment. However, strict frequency matching is required between the receiver and the transmitter to maximize the power transmission distance at a particular coil size. As the number of connected devices increases and the distance increases, the transmission power decreases. A separate two-way channel is required between the transmitter and each receiver, usually by Bluetooth.
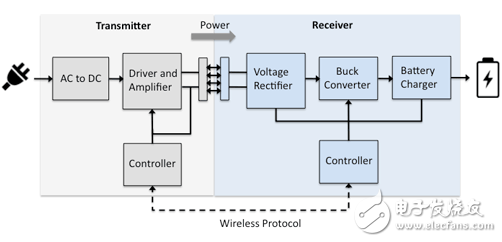
Figure 3 Near Field Resonance Charging System
Table 1 is a comparison table of three near-field charging standards for Qi, AirFuel InducTIve and AirFuel Resonant. It is worth noting that whether it is electromagnetic induction or resonant charging, the transmitter and receiver must be kept at the shortest distance.
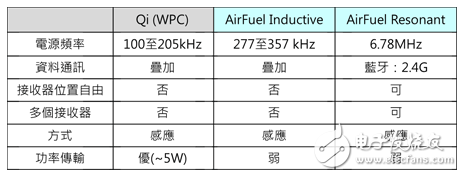
Table 1 Comparison of near-field charging standards
Due to two standards, General Motors (GM) announced that its vehicles will support both the AirFuel InducTIve and Qi standards. Samsung also decided that its phone will support two standards.
| About Bare Wire |
|
Application: Suitable for manufacturing electric motors, windings of electrical equipment, automobile electrical rotors, installation and distribution equipment and other electrical fields.

Name
Conductor
Copper
Dimension(mm)
Rectangular: Thickness(a): 0.90 ~ 5.60
Width(b): 3.15 ~ 16.00
Standard
GB;
Packing
160 kg~180 kg ply-wood spool(250*500; 250*600)
Application
Suitable for manufacturing electric motors, windings of electrical equipment, automobile electrical rotors, installation and distribution equipment and other electrical fields.
Bare wire includes Copper Bar and Aluminium bar
Bare Wire
Bare Wire,Bare Copper Wire For Motor,Flexible Bare Copper Wire,Electrical Bare Copper Wire
HENAN HUAYANG ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY GROUP CO.,LTD , https://www.huaonwire.com