In the morning's "News Tea Fan" segment, the topic of "Intel i3 finally introduces Turbo Boost" was discussed. A little partner in the message asked Rui what exactly Turbo Boost is. Today, Xiao Bian will share some insights on this topic.

What is Turbo Boost?
Turbo Boost, also known as boost frequency, is a technology that allows the CPU to temporarily increase its clock speed to improve performance. This is especially useful when running demanding applications that require more processing power. When the workload is light or when the CPU isn't under heavy load, it automatically lowers the frequency to save power and reduce heat. This dynamic adjustment ensures that the CPU delivers high performance when needed while maintaining efficiency and thermal control.
Typically, Turbo Boost can increase the CPU's frequency by around 20% above the base clock speed, allowing it to "surpass" the standard performance level and meet higher computational demands.
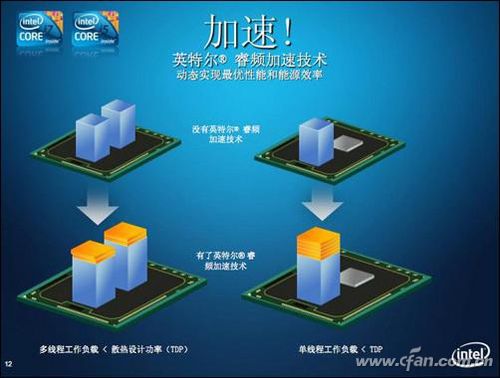
Is Turbo Boost the same as overclocking?
Some people might confuse Turbo Boost with overclocking, but they are quite different. While both involve increasing the CPU’s frequency, the key difference lies in how they are implemented.
Turbo Boost is a built-in feature that dynamically adjusts the CPU’s frequency and voltage based on real-time workload, all while staying within the processor’s defined power, current, voltage, and temperature limits. On the other hand, overclocking involves manually pushing the CPU beyond its designed specifications, often requiring increased voltage and cooling. This can lead to higher power consumption and potential instability, and it doesn’t adjust automatically based on the application’s needs.

Does the Power Wall Still Exist?
The recent announcement about the mobile i3 supporting Turbo Boost has raised questions about whether the power wall still exists. The term "power wall" refers to the maximum power a CPU can consume without overheating or causing damage. Once the CPU exceeds this limit, it may throttle itself to prevent damage.
Mobile CPUs, such as Intel’s U-series, typically have a TDP (Thermal Design Power) of 15W. Despite this limitation, manufacturers continue to push for better performance. The introduction of 10nm process technology helps achieve this, allowing for higher clock speeds without exceeding power limits. If the i3 were still using 14nm, achieving similar performance at 15W would be extremely challenging.

When Will Desktop Processors Get It?
The i3 with Turbo Boost is currently a low-voltage mobile CPU. Many users are wondering if desktop versions will also support this feature. From what we’ve observed, it seems unlikely for now. Desktop CPUs have higher TDPs, usually around 65W, and already run at very high base frequencies—like the i3-8100, which has a base clock of 3.6GHz. Adding Turbo Boost could significantly boost single-core performance, potentially making the i5 seem outdated. So, for now, it's not realistic for desktop i3s to adopt this feature.

Finally, in the morning, a little friend mentioned they didn’t know the difference between i3, i5, and i7. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Entry-level CPU: Intel Celeron, Pentium, AMD Ryzen APU
Mainstream CPU: Intel Core i3, AMD Ryzen 3
Mid-range CPU: Intel Core i5, AMD Ryzen 5
High-end CPU: Intel Core i7, AMD Ryzen 7
Flagship CPU: Intel Core i9, AMD Ryzen Pro, Ryzen Threadripper

Lithium batteries offer high energy density, longer lifespan, and lightweight design. They are widely used in portable electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage.
Rechargeable Unit, Energy storage, Portable electronics, Power tools
Bosin Power Limited , https://www.bosinsolar.com