Abstract: Radiation sources have strong social sensitivities. Whether they are discarded or leaked, they will cause immeasurable losses and harms to human society and the environment. In order to enable it to further benefit human society and regulate the use of radiation sources, safety regulation is particularly important. The article introduces a set of safety monitoring IoT application system integrating radiation source dose monitoring, RFID electronic tag, GPS earth positioning, displacement detection, video monitoring and management to reduce the risk of theft of radiation sources and achieve accurate and efficient radiation. The goal of source safety regulation.
Keywords: Internet of Things; radiation source; RFID; GPS; GPRS; video surveillance
introduction
With the rapid development of nuclear technology and information technology, the application market of radiation sources is becoming more and more extensive. Through applications in industry, agriculture, medicine, and research, radiation sources have provided tremendous benefits to humans and society, and have made important contributions to scientific and technological progress. At the same time, due to poor management of radiation sources, it has caused serious harm to the environment and human health. Traditional regulatory methods for radiation sources are lock-ups, warnings, and human care. However, human factors cause loss and leakage accidents, which pose a huge threat to society and public safety. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to establish a set of radiation source safety supervision system based on the Internet of Things, to connect the radiation source with the network for information exchange and communication, and to achieve intelligent identification, location, tracking, monitoring and management.
1 system overall architecture
The overall architecture of the radiation source security supervision system based on the Internet of Things consists of the front-end field part (sensing layer), the data transmission part (transport layer) and the security supervision part (application layer). Figure 1 shows the system structure diagram. Among them, the front-end field part is equipped with dose detection, RFID electronic tag identification, GPS positioning tracking, video monitoring and other devices on the premise of the radiation source to ensure that the radiation source has abnormalities such as loss, displacement and leakage, and send it to the supervision center through the transmission layer. Data and status signals and send alarm signals to local and supervisors on site. The data transmission part transmits the dose information and the electronic label information to the monitoring center through GPRS; transmits the video monitoring signal to the monitoring center through 3G, ADSL or dedicated line; transmits the mobile source location information to the monitoring center through GPS positioning and GPRS The mobile source video surveillance image is transmitted to the monitoring center via GPRS as a picture. The information processing analysis, intelligent application service and control decision are completed by the security supervision system of the monitoring center.
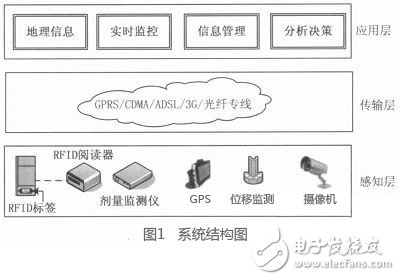
2 Design of the front-end sensing layer of the site
The front-end sensing layer of the site is mainly composed of hardware devices such as a dose detector, an anti-demolition RFID tag, an RFID reader, a displacement monitoring device, a high-definition network camera, and a network device.
2.1 Dose detection
The radiation intensity of each radiation source application site is measured using different types of gauges. Each monitor collects the measured data of the measured radioactive source through the photoelectric sensor. After A/D conversion, the measuring instrument transmits the obtained digital signal to the monitoring center through the wireless network. The monitoring center can determine whether the radiation source has an accident such as loss or dose leakage.
2.2 RFID electronic tags and readers
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) (RadioFrequencyIdenTIficaTIon) technology is an emerging automatic identification technology, which is the core technology of the Internet of Things. It uses wireless radio frequency for non-contact two-way data communication to achieve the purpose of identifying and exchanging data. RFID has the characteristics of long distance, simultaneous identification of multiple tags, fast recognition speed, large tag storage capacity, and data security. In this scheme, the RFID technology is used to realize the anti-theft alarm of the radiation source. The principle is shown in Figure 2.
If a tamper-evident RFID tag with an effective distance of less than 10 m is installed for each radiation source and an RFID reader is installed at a location not far from the source (eg, less than 10 m), the RFID reader will continuously read the data from the RFID. . Once the RFID tag is demolished, or the radiation source is moved more than 10m away from the RFID reader, the RFID reader will no longer be able to read the RFID data. At this point, the source is considered to be illegally moved and the alarm will automatically pass the SMS. The method sends an alarm message to a mobile phone of a specific number, and at the same time, sends an alarm message to the monitoring center through GPRS or CDMA or 3G network.
2.3 GPS (GlobalPosiTIoningSystem) Global Positioning System
The terminal equipment is composed of a GPS receiver, a GPRS transceiver module, etc. The GPS module is responsible for receiving satellite positioning (longitude, latitude and altitude) signals, and the GPRS module is responsible for completing wireless transmission of information. When the mobile radiation source is in use or transported, in order to realize reliable remote monitoring of the radiation source by the GPS terminal, GPS combines GIS (Geographical InformaTIonSystem) geographic information system to track the position of the radiation source in real time, and when the GPS work is abnormal, it passes The GIS system is marked with an alarm message on the corresponding map.
2.4 Displacement monitoring
When the radiation source package and the installation position are illegally displaced, the system will promptly report to the supervision center and the site to remind the relevant personnel on the site to take preventive measures in time.
2.5 HD network video surveillance
The application of video surveillance occupies a large proportion of the security field, and it is necessary to conduct real-time monitoring and video recording on the radiation source work site. Especially in some important places (such as water plants, power plant fixed sources and some special needs of mobile transportation sources), HD network video surveillance technology is generally adopted.
Surround Speakers,Home Theater Systems,Wooden Cabinet Speakers,Commercial Conference Speaker Systems
The ASI Audio Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.asi-sound.com