Out of the empty suburbs,
a highway with a relatively simple layout,
a closed training ground—
are these all the scenes where self-driving cars are tested?
When someone overtakes, and roads overlap,
is it impossible for a car to drive automatically?
I want to take a self-driving car for a ride, but if it's on a road shared with human-driven cars, how can it be both smooth and safe? That's where RSS comes in.
RSS stands for "Responsibility-Sensitive Safety." It's a practical framework that defines measurable safety parameters for autonomous vehicles. By analyzing data from real-world traffic accidents, RSS helps establish a clear definition of what constitutes a "safe state" for an autonomous vehicle. With this model, self-driving cars can simulate driving scenarios, drive cautiously, and even determine responsibility after an accident. This makes them capable of handling complex environments and taking you anywhere safely.

One of the biggest challenges in driving is maintaining a safe distance from the car in front. Imagine two cars on the same lane. If the front car brakes suddenly and the rear one can't stop in time, the rear car is at fault. Using the RSS model, we can precisely calculate the safe following distance based on factors like speed and braking capability. These values come from the car’s sensors, ensuring that the self-driving vehicle can avoid collisions safely.

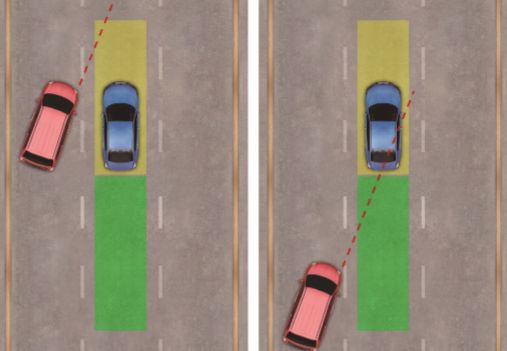
Overtaking is another complex situation. In some cases, the front car may overtake, and the rear car might hit it. In such situations, the front car is fully responsible. The RSS model ensures that autonomous vehicles maintain a safe distance from surrounding cars based on various factors. If a human driver doesn’t keep enough space and causes a collision, the responsibility lies with them. The AV calculates safe distances and avoids any actions that could lead to unsafe conditions.
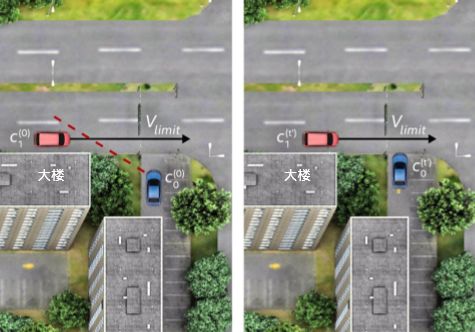
What about limited visibility or occluded objects? For example, when a car tries to enter a street from a parking lot, but a building blocks the view. Human drivers usually proceed slowly, gradually increasing their field of view. An autonomous vehicle with RSS does the same—it calculates the safest speed and entry point based on road conditions and sensor data. It also ensures that other vehicles have enough time to brake. If a collision happens due to a speeding car, the responsibility falls on the reckless driver.
In the case of a pedestrian crossing, the car is usually at fault, but not always. According to the RSS system, autonomous vehicles consider the possibility of a pedestrian suddenly running out between two parked cars. They adjust their speed accordingly to allow for timely braking and avoid hitting the pedestrian.
Beyond these scenarios, the RSS model also accounts for priority rules, two-way traffic, traffic lights, and unstructured roads. The goal is to eventually apply this model to all types of roads, providing a more complete safety framework for autonomous vehicles. One day, self-driving cars will be able to navigate city streets safely and smoothly, without obstacles or risks.
Fiber Cutter Tool,Fiber Cleaver Kit,Auto Return Cleaver,Single-mode fiber cleaver
Guangdong Tumtec Communication Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.gdtumtec.com